Articles
Keep your knowledge up to date!
Our team is browsing Pubmed daily to look for the latest research articles ultrasound. We try to summarize the most important articles for you in plain language. Below you can find 50+ short summaries.
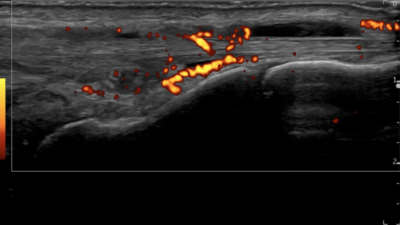
Understanding Neovascularization in Musculoskeletal Pathologies: Anatomical and Pathological Insights
Understanding Neovascularization in Musculoskeletal Pathologies: Anatomical and Pathological Insights
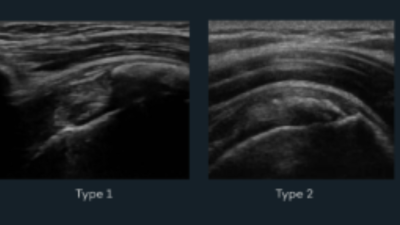
Ultrasound-Guided Barbotage of a Calcification: An Approach to Tendon Health
Ultrasound-Guided Barbotage of a Calcification: An Approach to Tendon Health

Monetizing Musculoskeletal Ultrasound in Physical Therapy in the USA
Monetizing Musculoskeletal Ultrasound in Physical Therapy in the USA
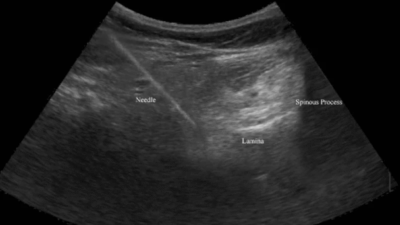
The Advantages of Musculoskeletal Ultrasound Over Fluoroscopy in Performing Spine Interventions
The Advantages of Musculoskeletal Ultrasound Over Fluoroscopy in Performing Spine Interventions
Common Applications of Musculoskeletal Ultrasound in Physical Therapy
Common Applications of Musculoskeletal Ultrasound in Physical Therapy
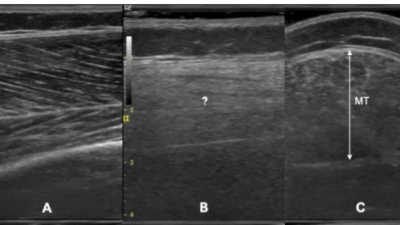
Musculoskeletal Ultrasound: A Guide to Assessing Muscular Dystrophy
Musculoskeletal Ultrasound: A Guide to Assessing Muscular Dystrophy
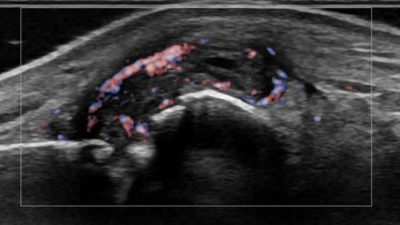
Musculoskeletal Ultrasound in the Diagnosis of Rheumatoid Arthritis
Musculoskeletal Ultrasound in the Diagnosis of Rheumatoid Arthritis
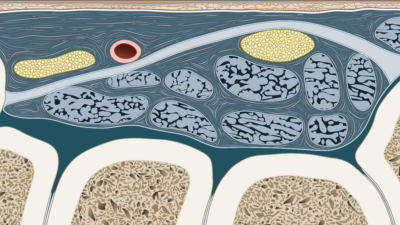
Musculoskeletal Ultrasound: A Tool for Evaluating Peripheral Nerve Disorders
Musculoskeletal Ultrasound: A Tool for Evaluating Peripheral Nerve Disorders
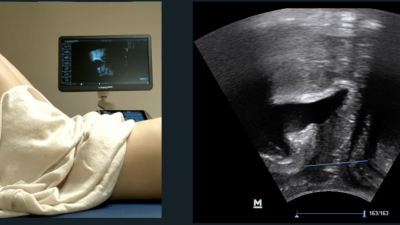
The Role of Musculoskeletal Ultrasound in Pelvic Floor Disorders and Rehabilitation
The Role of Musculoskeletal Ultrasound in Pelvic Floor Disorders and Rehabilitation
End of content
No more pages to load
